Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, affecting millions of people and posing a significant burden on healthcare systems. However, with the right knowledge and tools, it is possible to outsmart cardiovascular disease and maintain optimal heart health. This handbook provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, preventing, and managing cardiovascular disease, empowering readers to take control of their heart health and live a healthier, longer life.
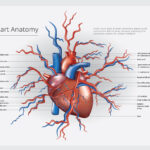
Understanding Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease refers to a group of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and stroke. These conditions are often caused by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, physical inactivity, and genetics.
The signs and symptoms of cardiovascular disease can vary depending on the specific condition, but may include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs, and irregular heartbeat. It is essential to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention immediately to prevent severe consequences.
Preventing Cardiovascular Disease
The good news is that many cases of cardiovascular disease can be prevented through lifestyle changes and management of risk factors. Here are some ways to outsmart cardiovascular disease:
1. Healthy Diet:
Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet.
2. Exercise Regularly:
Regular physical activity can help lower blood pressure, improve lipid profiles, reduce inflammation, and maintain a healthy weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both each week.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Excess weight, particularly around the waistline, increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise can help reduce this risk.
4. Manage Stress:
Chronic stress can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease by raising blood pressure and damaging the blood vessels. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
5. Quit Smoking:
Smoking is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and quitting can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. Seek professional help to quit smoking if needed.
6. Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive alcohol consumption can increase blood pressure, cause heart failure, and lead to cardiovascular disease. Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels (up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men).
Managing Cardiovascular Disease
If you have already been diagnosed with cardiovascular disease, it is essential to manage the condition effectively to prevent complications and improve quality of life. Here are some ways to manage cardiovascular disease:
1. Medications: Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for medications to manage conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or heart failure.
2. Lifestyle Changes: In addition to a healthy diet and regular exercise, manage stress, quit smoking, and limit alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of complications.
3. Monitoring: Regularly monitor your blood pressure, pulse, and weight, and report any changes to your healthcare provider.
4. Follow-Up Care: Attend all scheduled appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor your condition and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
5. Support: Join a support group or enlist the help of family and friends to cope with the emotional impact of cardiovascular disease.
Significant Health Concern
Cardiovascular disease is a significant health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. However, with the right knowledge and tools, it is possible to outsmart cardiovascular disease and maintain optimal heart health. By understanding the causes, preventing, and managing cardiovascular disease through lifestyle changes and effective management, you can reduce the risk of complications and live a healthier, longer life. Take control of your heart health today and start your journey to a healthier heart.
Cardiovascular Disease Specific Symptoms
here are some specific symptoms of cardiovascular disease:
1. Chest pain or discomfort:
This is the most common symptom of coronary artery disease, which occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. The pain can be described as pressure, tightness, or a squeezing sensation in the chest. The pain can also radiate to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
2. Shortness of breath:
If the heart is not pumping effectively, it can lead to shortness of breath, even when you are at rest or engaged in light physical activity. This symptom can also occur when the heart valves are damaged or diseased.
3. Fatigue:
Fatigue is a common symptom of heart failure, which occurs when the heart is not pumping effectively. It can also be a symptom of arrhythmias, which are abnormal heart rhythms.
4. Swelling:
When the heart is not pumping effectively, it can cause fluid buildup in the body, leading to swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet. This can also be a sign of heart failure.
5. Palpitations:
Palpitations are abnormal heartbeats that can feel like your heart is skipping a beat or racing. They can be a symptom of arrhythmias.
6. Dizziness or lightheadedness:
If the heart is not pumping enough blood to the brain, it can cause dizziness or lightheadedness. This can also be a symptom of arrhythmias.
7. Coughing up pink, foamy mucus:
This is a symptom of heart failure, which can occur when the heart is not pumping effectively and fluid builds up in the lungs.
8. Ankle swelling:
Fluid buildup in the body can cause swelling in the ankles, which can be a sign of heart failure.
9. Faster heart rate:
A faster heart rate than normal can be a symptom of arrhythmias.
10. Pain in the neck, jaw, throat, or back:
This can be a symptom of a heart attack, which occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked.
It’s important to note that some people may not experience any symptoms in the early stages of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, it’s essential to maintain regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your heart health and address any potential issues before they become severe.




















Pingback: Hypertension 101: Everything You Need to Know About High Blood Pressure - POST BLOGS
Pingback: Arteries Health: A Guide to Optimal Well-Being - POST BLOGS